
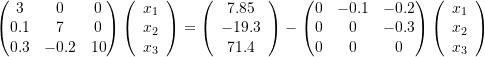
What mistakes did I make? I think it is in TriSolve method since if I replaced it with regular LU solver such as (np.linalg.solve) it works. Here, had been heading to compose a system program code for Gauss-Seidel method in MATLAB, discuss its theoretical history, and analyze the MATLAB programs end. Below is the same implementation in MATLAB which works: function x = gSeidel(A,B,N) For some reason it is not converging even after 50000 iterations to the solution even when the matrix A is strict diagonal dominant. #O(n) per iteration, so overall O(nN), good for large SPD/SDD matricesĪ = np.array(,])Īns = is my Gauss-Seidel method in Python. The algorithms will terminate when the change in x is less than tolerance, or if maxiter default200 iterations have been exceeded.

Not really important to your code (as you may be doing this for practice), but as you may already know, lu decomposition, already exists, for example ().There is no need to include the length of your objects in python, since python automatically stores the length of it's objects, which can always be retrieved with the len() builtin.For example, you can write to and read from an entire row or column all at once. This would greatly improve your code (and make it way faster) and make it way easier to read. I notice that you import numpy, but you don't use the operations for numpy arrays.If you don't use a variable in a list comprehension, then it is customary to use an _.Python only uses to place two lines of code on the same physical line. Python doesn't need to end a line, python knows when lines end.There are many things to address in your code:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
